User Guide
Duke The Market is a one-stop marketing tool that allows department stores to keep track of their upcoming marketing plan roll-outs, monitor its impact, and to target the appropriate subsegment of its customer base for each of those plans. It is also optimised for use via a Command Line Interface (CLI) while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI). If you can type fast, Duke The Market can help you organise your marketing events and reach out to your target customer base much faster than a traditional GUI app.
- Quick start
-
Features
- Instantaneous launching
- Saving the data
- Viewing help :
help - Adding a person:
addPerson - Listing all persons :
listPersons - Editing a person :
editPerson - Locating persons by name:
findPersons - Deleting a person :
deletePerson - Adding an event:
addEvent - Editing an event :
editEvent - Locating events by event title:
findEvents - Deleting an event:
deleteEvent - Listing all events:
listEvents - Tagging persons to an event :
tagEvent - Untagging persons from an event :
untagEvent - Creating mailing list for an event :
mailEvent - Generating pie chart statistic of the tagged persons of an event :
makeStats - Clearing all entries :
clear - Exiting the program :
exit - Editing the data file
- FAQ
- Command summary
Quick start
-
Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
dukeTheMarket.jarfrom here. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your application.
-
Double-click the file to start the app. The GUI similar to the below should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app contains some sample data.
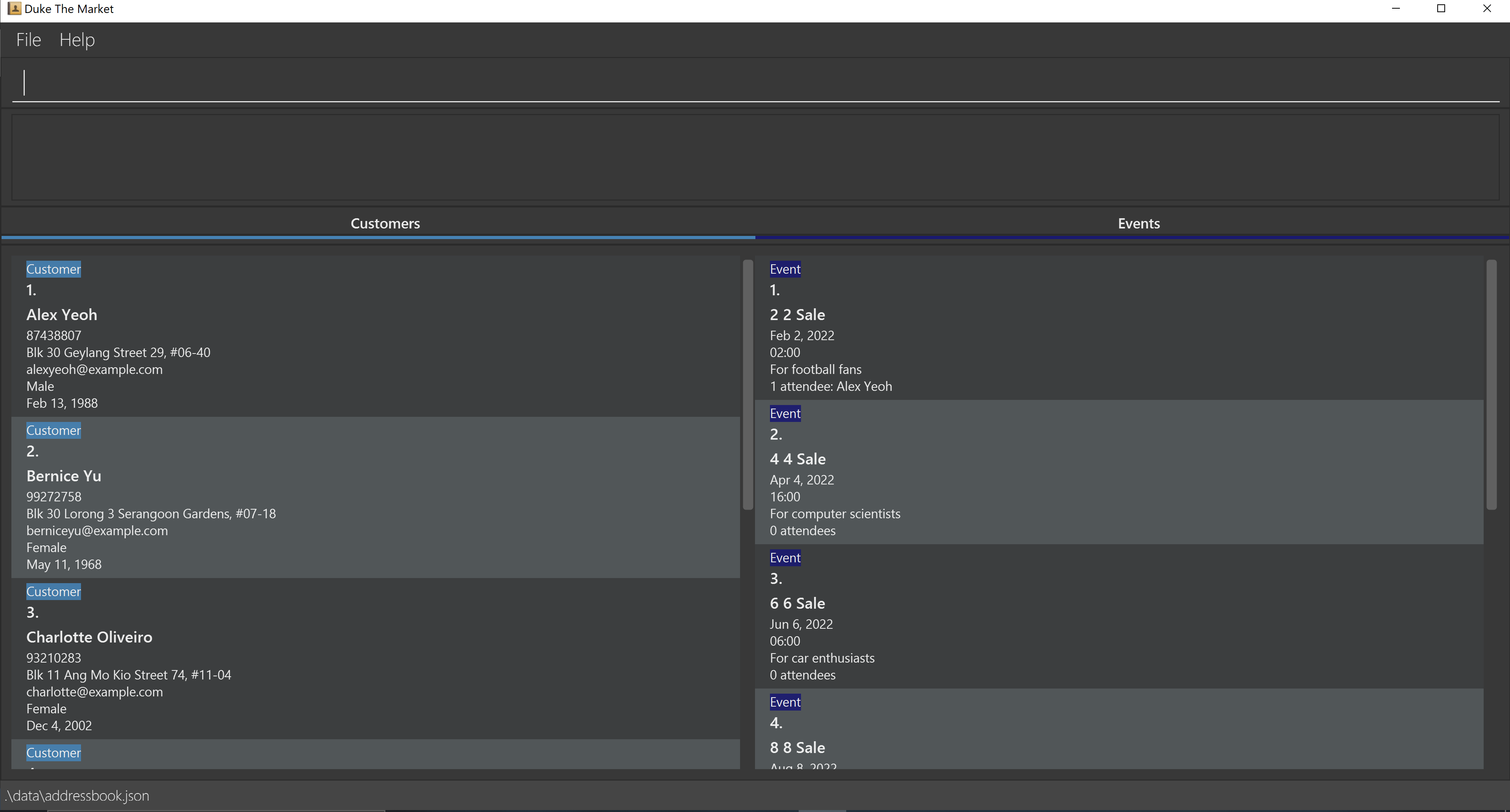
-
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. e.g. typing
helpand pressing Enter will open the help window.
Some example commands you can try:-
listPersons: Lists all persons. -
addPersonn/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01 g/m d/22/03/1993: Adds a person namedJohn Doeto the application. -
deletePerson3: Deletes the 3rd person shown in the current person list. -
clear: Deletes all persons and events. -
exit: Exits the app.
-
-
Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
Features
![]() Notes about the command format:
Notes about the command format:
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user.
e.g. inaddPerson n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used asaddPerson n/John. -
Parameters can be in any order.
e.g. if the command specifiesn/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER,p/PHONE_NUMBER n/NAMEis also acceptable. - If a parameter is specified multiple times, only the last occurrence of the parameter will be considered regardless of the validity of previous parameter inputs.
- e.g. if you specify
p/12341234 p/56785678, even though both are valid phone numbers, onlyp/56785678, will be taken by the command as its parameter input. - e.g. if you specify
d/A/B/C d/01/01/2022, even though the first parameter inputd/A/B/Cis invalid, onlyd/01/01/2022, which is a valid parameter input, will be taken by the command as its parameter input. - e.g. if you specify
d/01/01/2022 d/A/B/C, even though the first parameter inputd/01/01/2022is valid, onlyd/A/B/C, which is an invalid parameter input, is considered.
- e.g. if you specify
- Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
help,exitandclear) will be ignored.
e.g. if the command specifieshelp 123, it will be interpreted ashelp.
Instantaneous launching
Users that have Java 11 or above installed in their computers can launch the Duke The Market program by double-clicking on the file.
Saving the data
Duke The Market data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
Viewing help : help
Shows a message explaining how to access the help page.
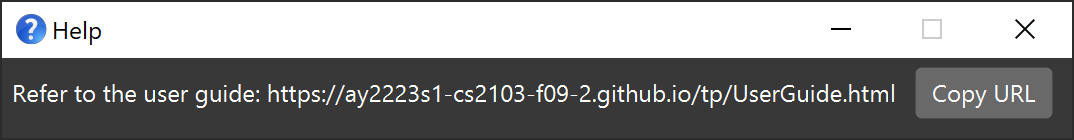
Format: help
Adding a person: addPerson
Adds a person to the application.
Format: addPerson n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS g/GENDER d/DOB
- The compulsory parameters are: name (
n), phone number (p), email (e), address (a), gender (g), date of birth(d). - Date format accepted is:
dd/mm/yyyy. - Date of birth cannot be after the current date.
- The genders accepted are:
M/m/Male/malefor male,F/f/Female/femalefor female.
Examples:
addPerson n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01 g/m d/20/03/2002addPerson n/Betsy Crowe e/betsycrowe@example.com a/Newgate Prison p/1234567 g/f d/14/12/1998
For example, if the application currently has a person named
Donny, the input addPerson n/Donny p/98765432 e/test@test.com a/UTown g/M d/10/10/2022
will not run and will output the error message This person already exists in the address book.
Listing all persons : listPersons
Shows a list of all persons in the application.
Format: listPersons [s/FIELD]
- Sorts all persons by a specified field.
FIELDmust take one of the following values:-
norN: sort by name in ascending lexicographical order, ignoring case differences -
dorD: sort by date of birth from oldest to youngest -
gorG: sort by gender, females first followed by males
-
- It is optional to include the sorting prefix and field. If the sorting prefix and field are not included, the application will display all persons in the current order that they are stored.
- At most one field can be specified. i.e. Cannot specify 2nd or 3rd criteria to sort by.
For example, if
listPersons s/n and listPersons are executed back-to-back, the result of the second listPersons command will display the sorted results from the first listPersons s/n command since the sorted result is permanent.
Examples:
-
listPersonsLists all persons without performing any sorting. -
listPersons s/nLists all persons sorted by their names.
Editing a person : editPerson
Edits an existing person in the application.
Format: editPerson PERSON_INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [g/GENDER] [d/DOB]
- Edits the person at the specified
PERSON_INDEX. ThePERSON_INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed person list. ThePERSON_INDEXmust be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …, and it must be within the range of the person list index. This command is invalid ifPERSON_INDEXis a non-positive integer. - Existing values will be updated to the input values.
- At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- Date format accepted is:
dd/mm/yyyy. - Date of birth cannot be after the current date.
- The genders accepted are:
M/m/Male/malefor male,F/f/Female/femalefor female.
Examples:
-
editPerson 1 p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.comEdits the phone number and email address of the 1st person to be91234567andjohndoe@example.comrespectively. -
editPerson 2 n/Betsy CrowerEdits the name of the 2nd person to beBetsy Crower. -
editPerson 3 n/Charlotte g/F d/03/04/1998Edits the 3rd person’s name to beCharlotte, gender to beFemaleand date of birth to be03/04/1998.
Locating persons by name: findPersons
Finds all persons whose names contain any of the given keywords.
Format: findPersons KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g.
hanswill matchHans. - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Hans Bowill matchBo Hans. - Only the name is searched.
- Only full words will be matched e.g.
Hanwill not matchHans. - Persons matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch). e.g.Hans Bowill returnHans Gruber,Bo Yang.
Examples:
-
findPersons JohnreturnsjohnandJohn Doe -
findPersons alex davidreturnsAlex Yeoh,David Li
Deleting a person : deletePerson
Deletes the specified person from the application.
Format: deletePerson PERSON_INDEX
- Deletes the person at the specified
PERSON_INDEX. - The
PERSON_INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed person list. - The
PERSON_INDEXmust be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …, and it must be within the range of the person list index. This command is invalid ifPERSON_INDEXis a non-positive integer.
Examples:
-
listPersonsfollowed bydeletePerson 2deletes the 2nd person in the application. -
findPersons Betsyfollowed bydeletePerson 1deletes the 1st person in the results of thefindPersonscommand.
Adding an event: addEvent
Adds a new event to the application.
Format: addEvent e/EVENT_TITLE d/DATE t/TIME p/PURPOSE
- The compulsory parameters are: event title (
e), date (d), time (t) and purpose (p). - Only alphanumeric characters are allowed for event title (
e). - Date format accepted is:
dd/mm/yyyy. - Date of event can be before, during and after current date.
- Time format accepted is:
hh:mm. - Any character is allowed for purpose (
p).
Examples:
addEvent e/Shoe Sale d/30/05/2022 t/11:00 p/30 dollar discount on all shoesaddEvent e/Banana Discount d/20/04/2022 t/14:00 p/20 cent discount on all bananas
For example, if the application currently has an event with an event title
Car Sale, the input addEvent e/Car Sale d/10/10/2022 t/10:40 p/5000 dollars off all cars
will not run and will output the error message This event already exists in the address book.
t/00:00 is allowed. Meanwhile, the input of t/24:00 is not allowed.
Editing an event : editEvent
Edits an existing event in the application.
Format: editEvent EVENT_INDEX [e/EVENT_TITLE] [d/DATE] [t/TIME] [p/PURPOSE]
- Edits the event at the specified
EVENT_INDEX. TheEVENT_INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed event list. TheEVENT_INDEXmust be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …, and it must be within the range of the event list index. This command is invalid ifEVENT_INDEXis a non-positive integer. - At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- Existing values will be updated to the input values.
- Only alphanumeric characters are allowed for event title (
e). - Date format accepted is:
dd/mm/yyyy. - Date of event can be before, during and after current date.
- Time format accepted is:
hh:mm. - Any character is allowed for purpose (
p).
Examples:
-
editEvent 1 e/Toy Dinosaur Sale t/10:10Edits the event title and time of the 1st event to beToy Dinosaur Saleand10:10respectively. -
editEvent 2 e/Pillow SaleEdits the event title of the 2nd event to bePillow Sale. -
editEvent 3 d/10/10/2022 p/20 dollars off bottlesEdits the 3rd event’s date and purpose to be10/10/2022and20 dollars off bottlesrespectively.
Locating events by event title: findEvents
Finds all events whose event titles contain any of the given keywords.
Format: findEvents KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g.
carswill matchCars - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Cars Salewill matchSale Cars - Only the event title is searched.
- Only full words will be matched e.g.
Carwill not matchCars - Events matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch). e.g.Car Salewill returnCar Discount,Marketing Sale
Examples:
-
findEvents SalereturnssaleandMarketing Sale -
findEvents sports carreturnsSports Festival,Car Sale
Deleting an event: deleteEvent
Deletes an existing event in the application.
Format: deleteEvent EVENT_INDEX
- Removes the event at the specified
EVENT_INDEX. - The
EVENT_INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed event list. - The
EVENT_INDEXmust be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …, and it must be within the range of the event list index. This command is invalid ifEVENT_INDEXis a non-positive integer.
Examples:
-
listEventsfollowed bydeleteEvent 2deletes the 2nd event in the application.
Listing all events: listEvents
Shows a list of all events in the application.
Format: listEvents [s/FIELD]
- Sorts the events by a specified field.
FIELDmust take one of the following values:-
eorE: sort by event title in ascending lexicographical order, ignoring case differences -
dorD: sort by date from oldest to newest
-
- It is optional to include the sorting prefix and field. If the sorting prefix and field are not included, the application will display all events in the current order that they are stored.
- At most one field can be specified. i.e. Cannot specify 2nd or 3rd criteria to sort by.
For example, if
listEvents s/e and listEvents are executed back-to-back, the result of the second listEvents command will display the sorted results from the first listEvents s/e command since the sorted result is permanent.
Examples:
-
listEventsLists all events without performing any sorting. -
listEvents s/eLists all events sorted by their event titles.
Tagging persons to an event : tagEvent
Format: tagEvent EVENT_INDEX p/PERSON_INDEX [MORE_PERSON_INDEXES] ...
- The
EVENT_INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed event list. - The
EVENT_INDEXmust be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …, and it must be within the range of the event list index. This command is invalid ifEVENT_INDEXis a non-positive integer. - The
PERSON_INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed person list. - The
PERSON_INDEXmust be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …, and it must be within the range of the person list index. - The
PERSON_INDEXmust refer to a person that is not currently tagged to the event. - Multiple
PERSON_INDEXs should be separated by white space. At least onePERSON_INDEXmust be provided. - Duplicate
PERSON_INDEXs are not allowed.
Example:
-
tagEvent 1 p/2tags the 2nd person in the person list to the 1st event in the event list. -
tagEvent 2 p/2 4 5tags the 2nd, 4th, 5th person in the person list to the 2nd event in the event list.
Untagging persons from an event : untagEvent
Format: untagEvent EVENT_INDEX p/PERSON_INDEX [MORE_PERSON_INDEXES] ...
- The
EVENT_INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed event list. - The
EVENT_INDEXmust be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …, and it must be within the range of the event list index. This command is invalid ifEVENT_INDEXis a non-positive integer. - The
PERSON_INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed person list. - The
PERSON_INDEXmust be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …, and it must be within the range of the person list index. - The
PERSON_INDEXmust refer to a person that is currently tagged to the event. - Multiple
PERSON_INDEXs should be separated by white space. At least onePERSON_INDEXmust be provided. - Duplicate
PERSON_INDEXs are not allowed.
Example:
-
untagEvent 1 p/2untags the 2nd person in the person list from the 1st event in the event list. -
untagEvent 2 p/2 4 5untags the 2nd, 4th, 5th person in the person list from the 2nd event in the event list.
Creating mailing list for an event : mailEvent
Format: mailEvent EVENT_INDEX
- The
EVENT_INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed event list. - The
EVENT_INDEXmust be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …, and it must be within the range of the event list index. This command is invalid ifEVENT_INDEXis a non-positive integer. - The mailing list is saved as a CSV file at the following location:
[JAR file location]/data/EVENT_TITLE.csv. The CSV file has 2 columns:NameandEmail, representing the name and email for every person tagged to the event.
Example:
-
mailEvent 2creates the mailing list as a CSV file, the name of the CSV file is the same as the title of the 2nd event in the event list.
Generating pie chart statistic of the tagged persons of an event : makeStats
Format: makeStats EVENT_INDEX t/STATISTIC_TYPE
- The
EVENT_INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed event list. - The
EVENT_INDEXmust be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …, and it must be within the range of the event list index. This command is invalid ifEVENT_INDEXis a non-positive integer. - The
STATISTIC_TYPErefers to the type of statistical data being generated and it must take one of the following values:-
agenerate a pie chart showing the distribution of ages across age groups. Each age group has a 5-year age range. -
ggenerate a pie chart showing the distribution of genders, separating them into eitherMaleorFemalecategories.
-
Example:
-
makeStats 1 t/ggenerates gender statistics of the persons tagged to the 1st event in the event list -
makeStats 3 t/agenerates age statistics of the persons tagged to the 3rd event in the event list
This issue is a bug pertaining to the JavaFX library.
Clearing all entries : clear
Clears all persons and events from the application.
Format: clear
Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
Editing the data file
The application’s data is saved as a JSON file [JAR file location]/data/addressbook.json. Advanced users are welcome to update data directly by editing the data file.
FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another computer?
A: Launch the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with your existing data file.
Q: I am unable to input a starting time for my event using the format specified. What should I do?
A: Change the language settings within your computer to a language that supports the “hh:mm” format.
Command summary
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| AddPerson |
addPerson n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS g/GENDER d/DOB e.g., addPerson n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01 g/m d/20/03/2002
|
| DeletePerson |
deletePerson PERSON_INDEXe.g., deletePerson 3
|
| EditPerson |
editPerson PERSON_INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [g/GENDER] [d/DOB]e.g., editPerson 2 n/James Lee e/jameslee@example.com
|
| FindPersons |
findPersons KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]e.g., findPersons James Jake
|
| ListPersons |
listPersons [s/FIELD] e.g., listPersons s/n
|
| AddEvent |
addEvent e/EVENT_TITLE d/DATE t/TIME p/PURPOSEe.g., addEvent e/Shoe Sale d/30/05/2022 t/11:00 p/30 dollar discount on all shoes
|
| DeleteEvent |
deleteEvent EVENT_INDEXe.g., deleteEvent 2
|
| EditEvent |
editEvent EVENT_INDEX [e/EVENT_TITLE] [d/DATE] [t/TIME] [p/PURPOSE]e.g., editEvent 2 e/Chocolate Sale p/10 dollars off all chocolates
|
| FindEvents |
findEvents KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]e.g., findEvents Sale Discount
|
| ListEvents |
listEvents [s/FIELD]e.g., listEvents s/e
|
| MakeStats |
makeStats EVENT_INDEX t/STATISTIC_TYPEe.g., makeStats 1 t/g
|
| MailEvent |
mailEvent EVENT_INDEXe.g., mailEvent 3
|
| TagEvent |
tagEvent EVENT_INDEX p/PERSON_INDEX [MORE_PERSON_INDEXES] e.g., tagEvent 2 p/1 3
|
| UntagEvent |
untagEvent EVENT_INDEX p/PERSON_INDEX [MORE_PERSON_INDEXES] e.g., untagEvent 3 p/4 5
|
| Clear | clear |
| Help | help |